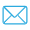
Novastar XA50 Pro High-end 5G Receiving Card Supports Resolutions up to 1024×512@60Hz For Large Full Color LED Display
Introduction
The XA50 Pro a high-end 5G receiving card in the new-generation control system COEX series of Xi'an NovaStar Tech Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as NovaStar). For 8bit and 10bit video sources and PWM driver ICs, a single XA50 Pro supports resolutions up to 1024×512@60Hz. For 12bit video sources, a single XA50 Pro supports resolutions up to 620×512@60Hz.
This receiving card supports the exclusive Adaptive Thermal Compensation, Dynamic Booster, Full-Grayscale Calibration, and Image Booster technologies of NovaStar. With other various functions, such as Multi-Mode, Brightness Overdrive, Seam Correction with Mobile Phones, Frame Rate Adaptive 3.0, Shutter Fit, HDR, Pixel Level Brightness and Chroma Calibration, Quick Adjustment of Dark or Bright Lines, Low Latency, 3D, and 90° Image Rotation, this receiving card can greatly improve the brightness, grayscale and color performance from every aspect, offering users an ultimate visual experience with a uniform, smooth and lifelike image. The product supports the usage of NCP files, enabling users to conveniently and swiftly carry out tasks such as displaying content on the cabinets, upgrading firmware, and optimizing image quality.
The XA50 Pro uses DDR3 connectors for communication. It is small, flexible, highly integrated, and therefore convenient for cabinet structure design. It can handle up to 40 groups of parallel RGB data or 64 groups of serial data and also supports LVDS transmission.
Certifications
RoHS, EMC Class A.
Features
Improvements to Display Effect
. Adaptive Thermal Compensation
Dynamically adjust the thermal compensation coefficients of the screen to address the issue of color cast caused by uneven heat dissipation across the screen.
. Dynamic Booster
Real-time analysis and dynamic adjustment are made to each frame to significantly improve the display contrast and image details for better visual experience, and effectively control and lower the display power consumption, extending the service life of the LED screen.
. Full-Grayscale Calibration
Work with NovaStar’s high-precision calibration system and the C3200 scientific grade camera to generate unique calibration coefficients for each grayscale, ensuring uniformity of each grayscale and dramatically improving the image quality.
. Image Booster (Effects depend on driver IC)
- Color Management: Support standard (Rec.709 / DCI-P3 / Rec.2020) and custom color gamuts, enabling more precise colors on the screen.
- Precise Grayscale: Individually correct the 65,536 levels of grayscale (16bit) of the driver IC to fix the display problems at low grayscale conditions, such as brightness spikes, brightness dips, color cast and mottling. This function can also better assist other display technologies, such as 22bit+ and individual gamma adjustment for RGB, allowing for a smoother and uniform image.
- 22bit+: Improve the LED screen grayscale by 64 times to avoid grayscale loss due to low brightness and allow for a smoother image with more details in dark areas.
. Multi-Mode
Apply different modes based on different display scenarios. This ensures that LED screens are able to achieve optimal display quality in various scenarios.
. Brightness Overdrive
Enhance the maximum brightness of the screen by balancing the uniformity, thus increasing the dynamic range and improving image contrast.
. Seam Correction with Mobile Phones
The brightness discrepancies in seams caused by splicing modules or cabinets can be automatically or manually adjusted via mobile phone software, enhancing the overall visual experience. (Requires working with the TU series products)
. Frame Rate Adaptive 3.0
Adjust the receiving card parameters in real time according to the input frame rate, so that the display effect at different frame rates (23 Hz to 240 Hz) is the best.
. Shutter Fit
Automatically adjust the driver IC parameters according to the camera shutter angle to fix problems of black lines, grayscale addition, and grayscale loss during camera shooting in xR scenarios.
. HDR
- Support HDR10 and comply with the SMPTE ST 2084 and SMPTE ST 2086 standards.
- Support HLG.
. Pixel Level Brightness and Chroma Calibration
Work with NovaStar's high-precision calibration system to calibrate the brightness and chroma of each pixel, effectively eliminating differences and enabling high consistency for both brightness and chroma.
. Quick Adjustment of Dark or Bright Lines
The different brightness of seams caused by splicing of modules or cabinets can be corrected to improve the visual experience. The adjustment can be in milliseconds.
. Low Latency
The latency of video source on the receiving card end can be reduced to 1 frame (only when using modules with driver IC with built-in RAM).
. 3D
Work with the controller that supports 3D function to enable 3D output.
. 90° Image Rotation
The display image can be rotated in multiples of 90° (0°/90°/180°/270°).
Improvements to Maintainability
. Calibration Coefficient Management
The calibration coefficients can be uploaded very fast, read back, and saved to hardware.
. Automatic Module Calibration
After a new module with flash memory is installed to replace the old one, the calibration coefficients stored in the flash memory can be automatically uploaded to the receiving card when it is powered on, which ensures unchanged uniform display brightness and chroma.
. Module Flash Management
For modules with flash memory, the information stored in the memory can be managed. The calibration coefficients and module ID can be stored and read back.
. Quick Uploading of Calibration Coefficients
Upload the calibration coefficients quickly to the receiving cards to improve efficiency.
. One-click to Apply Calibration Coefficients in Module Flash
For modules with flash memory, when the Ethernet cable is disconnected, users can hold down the self-test button on the cabinet to upload the calibration coefficients in the memory of the module to the receiving card.
. Mapping 1.1
The cabinets can display the controller number, receiving card number, and Ethernet port information, allowing users to easily obtain the locations and connection topology of receiving cards.
. Temperature and Voltage Monitoring
Real-time monitoring of the temperature and voltage of the receiving card, without the need for other external devices.
. Bit Error Detection
Real-time monitoring of the communication of the Ethernet port on the receiving card. It records the number of error data packets, which helps users identify faults and troubleshoot network communication issues.
. Status Detection of Dual Power Supplies
When two power supplies are used, their working status can be detected.
. LVDS Transmission (dedicated firmware required)
Low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) transmission is used to reduce the number of data cables from the hub board to module, increasing the transmission distance and improving the signal transmission quality.
Improvements to Reliability
. Dual Card Backup and Status Monitoring
In an application requiring high reliability, two receiving cards can be mounted onto a single hub board for backup. When the primary card fails, the backup card can serve immediately to ensure uninterrupted operation of the display.
The working status of the primary and backup receiving cards can be monitored in real-time.
. Loop Backup
The receiving card and controller form a loop via the primary and backup line connections. When a fault occurs at a location of the lines, the screen can still display the image normally.
. Dual Backup of Configuration Parameters
The receiving card configuration parameters are stored in the application area and factory area of the receiving card at the same time. Users usually use the configuration parameters in the application area. If necessary, users can restore the configuration parameters in the factory area to the application area.
. Dual Program Backup
Two copies of firmware program are stored in the receiving card at the factory to avoid the problem that the receiving card may get stuck abnormally during program update.
. One-click Firmware Program Learning
The cabinet firmware program and configuration file can be copied to other cabinets with one click to help quickly complete cabinet configuration.
Appearance

All product pictures shown in this document are for illustration purpose only. Actual product may vary.
Indicators
| Indicators | Color | Status | Description |
| Running indicator | Green | Flashing once
every 1s |
The receiving card is functioning normally. Ethernet cable connection is normal, and video source input is available. |
| Flashing once
every 3s |
Ethernet cable connection is abnormal. | ||
| Flashing 3 times
every 0.5s |
Ethernet cable connection is normal, but video source input is unavailable. | ||
| Flashing once
every 0.2s |
The receiving card failed to load the
program in the application area and is now using the backup program. |
||
| Flashing 8 times
every 0.5s |
A redundancy switchover occurred on the Ethernet port and the loop backup has taken effect. | ||
| Power indicator | Red | Always on | The power input is normal. |
Dimensions
The board thickness is not greater than 1.5 mm, and the total thickness (board thickness + thickness of components on the top and bottom sides) is not greater than 5.0 mm. Ground connection (GND) is enabled for mounting holes.

Tolerance: ±0.3 Unit: mm
Note:
To make molds or trepan mounting holes, please contact NovaStar for a higher-precision structural drawing.
PINS
LVDS Pins

| LVDS Pin Definitions | |||||
| / | GND | 1 | 2 | GND | / |
| SerDes signal input (receiving cardoutput) | MGTP_TX1_N | 3 | 4 | MGTP_TX3_N | SerDes signal input (receiving card output) |
| MGTP_TX1_P | 5 | 6 | MGTP_TX3_P | ||
| / | GND | 7 | 8 | GND | / |
| SerDes signal output (receiving cardinput) | MGTP_RX1_N | 9 | 10 | MGTP_RX3_N | SerDes signaloutput (receiving card input) |
| MGTP_RX1_P | 11 | 12 | MGTP_RX3_P | ||
| / | GND | 13 | 14 | GND | / |
| LVDS Pin Definitions | |||||
| SerDes signal input (receiving cardoutput) | MGTP_TX2_N | 15 | 16 | MGTP_TX4_N | SerDes signal input (receiving card output) |
| MGTP_TX2_P | 17 | 18 | MGTP_TX4_P | ||
| / | GND | 19 | 20 | GND | / |
| SerDes signal output (receiving cardinput) | MGTP_RX2_N | 21 | 22 | MGTP_RX4_N | SerDes signaloutput (receiving card input) |
| MGTP_RX2_P | 23 | 24 | MGTP_RX4_P | ||
| / | GND | 25 | 26 | GND | / |
| PHY configuration clock | PHY_MDCLK | 27 | 28 | PHY_RST | PHY reset |
| PHY configuration data | PHY_MDIO | 29 | 30 | MCU_GPIO | Reserved |
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_1_N | 31 | 32 | LVDS1.8_27_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_1_P | 33 | 34 | LVDS1.8_27_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_2_N | 35 | 36 | LVDS1.8_28_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_2_P | 37 | 38 | LVDS1.8_28_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_3_N | 39 | 40 | LVDS1.8_29_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_3_P | 41 | 42 | LVDS1.8_29_P | ||
| / | GND | 43 | 44 | GND | / |
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_4_N | 45 | 46 | LVDS1.8_30_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_4_P | 47 | 48 | LVDS1.8_30_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_5_N | 49 | 50 | LVDS1.8_31_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_5_P | 51 | 52 | LVDS1.8_31_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_6_N | 53 | 54 | LVDS1.8_32_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_6_P | 55 | 56 | LVDS1.8_32_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_7_N | 57 | 58 | LVDS1.8_33_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_7_P | 59 | 60 | LVDS1.8_33_P | ||
| / | GND | 61 | 62 | GND | / |
| LVDS Pin Definitions | |||||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_8_N | 63 | 64 | LVDS1.8_34_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_8_P | 65 | 66 | LVDS1.8_34_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_9_N | 67 | 68 | LVDS1.8_35_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_9_P | 69 | 70 | LVDS1.8_35_P | ||
| Reserved (1.8 V) | GPIO1_ 1V8 | 71 | 72 | GPIO3_1V8 | Reserved (1.8 V) |
| GPIO2_ 1V8 | 73 | 74 | GPIO4_1V8 | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_10_N | 75 | 76 | LVDS1.8_36_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_10_P | 77 | 78 | LVDS1.8_36_P | ||
| / | GND | 79 | 80 | GND | / |
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_11_N | 81 | 82 | LVDS1.8_37_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_11_P | 83 | 84 | LVDS1.8_37_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_12_N | 85 | 86 | LVDS1.8_38_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_12_P | 87 | 88 | LVDS1.8_38_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_13_N | 89 | 90 | LVDS1.8_39_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_13_P | 91 | 92 | LVDS1.8_39_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_14_N | 93 | 94 | LVDS1.8_40_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_14_P | 95 | 96 | LVDS1.8_40_P | ||
| / | GND | 97 | 98 | GND | / |
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_15_N | 99 | 100 | LVDS1.8_41_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_15_P | 101 | 102 | LVDS1.8_41_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_16_N | 103 | 104 | LVDS1.8_42_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_16_P | 105 | 106 | LVDS1.8_42_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_17_N | 107 | 108 | LVDS1.8_43_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_17_P | 109 | 110 | LVDS1.8_43_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_18_N | 111 | 112 | LVDS1.8_44_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_18_P | 113 | 114 | LVDS1.8_44_P | ||
| LVDS Pin Definitions | |||||
| / | GND | 115 | 116 | GND | / |
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_19_N | 117 | 118 | LVDS1.8_45_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_19_P | 119 | 120 | LVDS1.8_45_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_20_N | 121 | 122 | LVDS1.8_46_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_20_P | 123 | 124 | LVDS1.8_46_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_21_N | 125 | 126 | LVDS1.8_47_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_21_P | 127 | 128 | LVDS1.8_47_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_22_N | 129 | 130 | LVDS1.8_48_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_22_P | 131 | 132 | LVDS1.8_48_P | ||
| / | GND | 133 | 134 | GND | / |
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_23_N | 135 | 136 | LVDS1.8_49_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_23_P | 137 | 138 | LVDS1.8_49_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_24_N | 139 | 140 | LVDS1.8_50_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_24_P | 141 | 142 | LVDS1.8_50_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_25_N | 143 | 144 | LVDS1.8_51_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_25_P | 145 | 146 | LVDS1.8_51_P | ||
| LVDS signal | LVDS1.8_26_N | 147 | 148 | LVDS1.8_52_N | LVDS signal |
| LVDS1.8_26_P | 149 | 150 | LVDS1.8_52_P | ||
| / | GND | 151 | 152 | GND | / |
| Reserved | GPIO1 | 153 | 154 | GPIO2 | Reserved |
| GPIO3 | 155 | 156 | GPIO4 | ||
| GPIO5 | 157 | 158 | GPIO6 | ||
| GPIO7 | 159 | 160 | GPIO8 | ||
| GPIO9 | 161 | 162 | GPIO10 | ||
| GPIO11 | 163 | 164 | GPIO12 | ||
| GPIO13 | 165 | 166 | GPIO14 | ||
| LVDS Pin Definitions | |||||
| GPIO15 | 167 | 168 | GPIO16 | ||
| / | GND | 169 | 170 | GND | / |
| Reserved | GPIO17 | 171 | 172 | GPIO18 | Reserved |
| GPIO19 | 173 | 174 | GPIO20 | ||
| GPIO21 | 175 | 176 | GPIO22 | ||
| GPIO23 | 177 | 178 | GPIO24 | ||
| GPIO25 | 179 | 180 | GPIO26 | ||
| GPIO27 | 181 | 182 | GPIO28 | ||
| GPIO29 | 183 | 184 | GPIO30 | ||
| GPIO31 | 185 | 186 | GPIO32 | ||
| GPIO33 | 187 | 188 | Input_KEY | Test button | |
| Tri-color LED | STA_LEDR- | 189 | 190 | STA_LEDG- | Tri-color LED |
| STA_LEDB- | 191 | 192 | MCU_SDA | I2C SDA | |
| ADC detection | MCU_ADC1 | 193 | 194 | MCU_SCL | I2C SCL |
| MCU_ADC2 | 195 | 196 | GND | / | |
| / | NC | 197 | 198 | NC | / |
| / | EXT_5V | 199 | 200 | EXT_5V | / |
| EXT_5V | 201 | 202 | EXT_5V | ||
| EXT_5V | 203 | 204 | EXT_5V | ||
40 Groups of Parallel RGB Data

| 40 Groups of Parallel RGB Data Pin Definitions | |||||
| / | GND | 1 | 2 | GND | / |
| SerDes signal input (receiving card
output) |
MGTP_TX1_N | 3 | 4 | MGTP_TX3_N | SerDes signal input (receiving card
output) |
| MGTP_TX1_P | 5 | 6 | MGTP_TX3_P | ||
| / | GND | 7 | 8 | GND | / |
| SerDes signal
output (receiving card input) |
MGTP_RX1_N | 9 | 10 | MGTP_RX3_N | SerDes signal
output (receiving card input) |
| MGTP_RX1_P | 11 | 12 | MGTP_RX3_P | ||
| / | GND | 13 | 14 | GND | / |
| SerDes signal input (receiving card
output) |
MGTP_TX2_N | 15 | 16 | MGTP_TX4_N | SerDes signal input (receiving card
output) |
| MGTP_TX2_P | 17 | 18 | MGTP_TX4_P | ||
| 40 Groups of Parallel RGB Data Pin Definitions | |||||
| / | GND | 19 | 20 | GND | / |
| SerDes signal
output (receiving card input) |
MGTP_RX2_N | 21 | 22 | MGTP_RX4_N | SerDes signal
output (receiving card input) |
| MGTP_RX2_P | 23 | 24 | MGTP_RX4_P | ||
| / | GND | 25 | 26 | GND | / |
| PHY configuration clock | PHY_MDCLK | 27 | 28 | PHY_RST | PHY reset |
| PHY configuration data | PHY_MDIO | 29 | 30 | MCU_GPIO | Reserved |
| Line decoding
signal |
A | 31 | 32 | BUFFER_EN | 245 driver IC
enable pin |
| B | 33 | 34 | READBACK_EN | 245 direction
control signal |
|
| C | 35 | 36 | RFU1 | Reserved | |
| D | 37 | 38 | LAT1 | Latch signal. | |
| Reserved | RFU2 | 39 | 40 | RFU3 | Reserved |
| Shift clock | DCLK1 | 41 | 42 | GCLK1 | Grayscale clock. |
| / | GND | 43 | 44 | GND | / |
| / | R1 | 45 | 46 | G1 | / |
| B1 | 47 | 48 | R2 | ||
| G2 | 49 | 50 | B2 | ||
| R3 | 51 | 52 | G3 | ||
| B3 | 53 | 54 | R4 | ||
| G4 | 55 | 56 | B4 | ||
| R5 | 57 | 58 | G5 | ||
| B5 | 59 | 60 | R6 | ||
| / | GND | 61 | 62 | GND | / |
| / | G6 | 63 | 64 | B6 | / |
| 40 Groups of Parallel RGB Data Pin Definitions | |||||
| R7 | 65 | 66 | G7 | ||
| B7 | 67 | 68 | R8 | ||
| G8 | 69 | 70 | B8 | ||
| R9 | 71 | 72 | G9 | ||
| B9 | 73 | 74 | R10 | ||
| G10 | 75 | 76 | B10 | ||
| R11 | 77 | 78 | G11 | ||
| / | GND | 79 | 80 | GND | / |
| / | B11 | 81 | 82 | R12 | / |
| G12 | 83 | 84 | B12 | ||
| R13 | 85 | 86 | G13 | ||
| B13 | 87 | 88 | R14 | ||
| G14 | 89 | 90 | B14 | ||
| R15 | 91 | 92 | G15 | ||
| B15 | 93 | 94 | R16 | ||
| G16 | 95 | 96 | B16 | ||
| / | GND | 97 | 98 | GND | / |
| / | R17 | 99 | 100 | G17 | / |
| B17 | 101 | 102 | R18 | ||
| G18 | 103 | 104 | B18 | ||
| R19 | 105 | 106 | G19 | ||
| B19 | 107 | 108 | R20 | ||
| G20 | 109 | 110 | B20 | ||
| R21 | 111 | 112 | G21 | ||
| B21 | 113 | 114 | R22 | ||
| / | GND | 115 | 116 | GND | / |
| 40 Groups of Parallel RGB Data Pin Definitions | |||||
| / | G22 | 117 | 118 | B22 | / |
| R23 | 119 | 120 | G23 | ||
| B23 | 121 | 122 | R24 | ||
| G24 | 123 | 124 | B24 | ||
| R25 | 125 | 126 | G25 | ||
| B25 | 127 | 128 | R26 | ||
| G26 | 129 | 130 | B26 | ||
| R27 | 131 | 132 | G27 | ||
| / | GND | 133 | 134 | GND | / |
| / | B27 | 135 | 136 | R28 | / |
| G28 | 137 | 138 | B28 | ||
| R29 | 139 | 140 | G29 | ||
| B29 | 141 | 142 | R30 | ||
| G30 | 143 | 144 | B30 | ||
| R31 | 145 | 146 | G31 | ||
| B31 | 147 | 148 | R32 | ||
| G32 | 149 | 150 | B32 | ||
| / | GND | 151 | 152 | GND | / |
| / | R33 | 153 | 154 | G33 | / |
| B33 | 155 | 156 | R34 | ||
| G34 | 157 | 158 | B34 | ||
| R35 | 159 | 160 | G35 | ||
| B35 | 161 | 162 | R36 | ||
| G36 | 163 | 164 | B36 | ||
| R37 | 165 | 166 | G37 | ||
| B37 | 167 | 168 | R38 | ||
| 40 Groups of Parallel RGB Data Pin Definitions | |||||
| / | GND | 169 | 170 | GND | / |
| / | G38 | 171 | 172 | B38 | / |
| R39 | 173 | 174 | G39 | ||
| B39 | 175 | 176 | R40 | ||
| G40 | 177 | 178 | B40 | ||
| Flash control pin | CODE1 | 179 | 180 | SPI_CLK | Clock signal of
serial pin |
| CODE2 | 181 | 182 | SPI_CS | CS signal of serial pin | |
| CODE3 | 183 | 184 | SPI_MISO | Module flash data storage output | |
| CODE4 | 185 | 186 | SPI_MOSI | Module flash data storage input | |
| CODE5 | 187 | 188 | Input_KEY | Test button | |
| Tri-color LED | STA_LEDR- | 189 | 190 | STA_LEDG- | Tri-color LED |
| STA_LEDB- | 191 | 192 | MCU_SDA | I2C SDA | |
| ADC detection | MCU_ADC1 | 193 | 194 | MCU_SCL | I2C SCL |
| MCU_ADC2 | 195 | 196 | GND | / | |
| / | NC | 197 | 198 | NC | / |
| / | EXT_5V | 199 | 200 | EXT_5V | / |
| EXT_5V | 201 | 202 | EXT_5V | ||
| EXT_5V | 203 | 204 | EXT_5V | ||
64 Groups of Serial Data

| 64 Groups of Serial Data Pin Definitions | |||||
| / | GND | 1 | 2 | GND | / |
| SerDes signal input (receiving card
output) |
MGTP_TX1_N | 3 | 4 | MGTP_TX3_N | SerDes signal input (receiving card output) |
| MGTP_TX1_P | 5 | 6 | MGTP_TX3_P | ||
| / | GND | 7 | 8 | GND | / |
| SerDes signal output (receiving card
input) |
MGTP_RX1_N | 9 | 10 | MGTP_RX3_N | SerDes signal
output (receiving card input) |
| MGTP_RX1_P | 11 | 12 | MGTP_RX3_P | ||
| / | GND | 13 | 14 | GND | / |
| SerDes signal input (receiving card
output) |
MGTP_TX2_N | 15 | 16 | MGTP_TX4_N | SerDes signal input (receiving card output) |
| MGTP_TX2_P | 17 | 18 | MGTP_TX4_P | ||
| 64 Groups of Serial Data Pin Definitions | |||||
| / | GND | 19 | 20 | GND | / |
| SerDes signal output (receiving card
input) |
MGTP_RX2_N | 21 | 22 | MGTP_RX4_N | SerDes signal
output (receiving card input) |
| MGTP_RX2_P | 23 | 24 | MGTP_RX4_P | ||
| / | GND | 25 | 26 | GND | / |
| PHY configuration clock | PHY_MDCLK | 27 | 28 | PHY_RST | PHY reset |
| PHY configuration data | PHY_MDIO | 29 | 30 | MCU_GPIO | Reserved |
| Line decoding signal | A | 31 | 32 | BUFFER_EN | 245 driver IC
enable pin |
| B | 33 | 34 | READBACK_EN | 245 direction
control signal |
|
| C | 35 | 36 | RFU1 | Reserved | |
| D | 37 | 38 | LAT1 | Latch signal. | |
| Reserved | RFU2 | 39 | 40 | RFU3 | Reserved |
| Shift clock | DCLK1 | 41 | 42 | GCLK1 | Grayscale clock. |
| / | GND | 43 | 44 | GND | / |
| / | DATA1 | 45 | 46 | DATA33 | / |
| DATA2 | 47 | 48 | DATA34 | ||
| DATA3 | 49 | 50 | DATA35 | ||
| DATA4 | 51 | 52 | DATA36 | ||
| DATA5 | 53 | 54 | DATA37 | ||
| DATA6 | 55 | 56 | DATA38 | ||
| DATA7 | 57 | 58 | DATA39 | ||
| DATA8 | 59 | 60 | DATA40 | ||
| / | GND | 61 | 62 | GND | / |
| / | DATA9 | 63 | 64 | DATA41 | / |
| 64 Groups of Serial Data Pin Definitions | |||||
| DATA10 | 65 | 66 | DATA42 | ||
| DATA11 | 67 | 68 | DATA43 | ||
| DATA12 | 69 | 70 | DATA44 | ||
| DATA13 | 71 | 72 | DATA45 | ||
| DATA14 | 73 | 74 | DATA46 | ||
| DATA15 | 75 | 76 | DATA47 | ||
| DATA16 | 77 | 78 | DATA48 | ||
| / | GND | 79 | 80 | GND | / |
| / | DATA17 | 81 | 82 | DATA49 | / |
| DATA18 | 83 | 84 | DATA50 | ||
| DATA19 | 85 | 86 | DATA51 | ||
| DATA20 | 87 | 88 | DATA52 | ||
| DATA21 | 89 | 90 | DATA53 | ||
| DATA22 | 91 | 92 | DATA54 | ||
| DATA23 | 93 | 94 | DATA55 | ||
| DATA24 | 95 | 96 | DATA56 | ||
| / | GND | 97 | 98 | GND | / |
| / | DATA25 | 99 | 100 | DATA57 | / |
| DATA26 | 101 | 102 | DATA58 | ||
| DATA27 | 103 | 104 | DATA59 | ||
| DATA28 | 105 | 106 | DATA60 | ||
| DATA29 | 107 | 108 | DATA61 | ||
| DATA30 | 109 | 110 | DATA62 | ||
| DATA31 | 111 | 112 | DATA63 | ||
| DATA32 | 113 | 114 | DATA64 | ||
| / | GND | 115 | 116 | GND | / |
| 64 Groups of Serial Data Pin Definitions | |||||
| / | NC | 117 | 118 | NC | / |
| NC | 119 | 120 | NC | ||
| NC | 121 | 122 | NC | ||
| NC | 123 | 124 | NC | ||
| NC | 125 | 126 | NC | ||
| NC | 127 | 128 | NC | ||
| NC | 129 | 130 | NC | ||
| NC | 131 | 132 | NC | ||
| / | GND | 133 | 134 | GND | / |
| / | NC | 135 | 136 | NC | / |
| NC | 137 | 138 | NC | ||
| NC | 139 | 140 | NC | ||
| NC | 141 | 142 | NC | ||
| NC | 143 | 144 | NC | ||
| NC | 145 | 146 | NC | ||
| NC | 147 | 148 | NC | ||
| NC | 149 | 150 | NC | ||
| / | GND | 151 | 152 | GND | / |
| Clock signal of serial pin | SPI_CLK | 153 | 154 | SPI_MOSI | Module flash data storage input |
| CS signal of serial pin | SPI_CS1 | 155 | 156 | MS_ID | Dual card backup identifier signal |
| Module flash data storage output | SPI_MISO1 | 157 | 158 | MS_DATA | Dual card backup connection signal |
| CS signal of serial pin | SPI_CS2 | 159 | 160 | Power_DET1 | Dual power
supply detection signal |
| Module flash data | SPI_MISO2 | 161 | 162 | Power_DET2 | |
| 64 Groups of Serial Data Pin Definitions | |||||
| storage output | |||||
| CS signal of serial pin | SPI_CS3 | 163 | 164 | Power_EN | Power enable
signal |
| Module flash data storage output | SPI_MISO3 | 165 | 166 | RFU4 | Reserved |
| CS signal of serial pin | SPI_CS4 | 167 | 168 | RFU5 | |
| / | GND | 169 | 170 | GND | / |
| Module flash data storage output | SPI_MISO4 | 171 | 172 | LDM_Temp_SS1 | Module
temperature detection chip selection signal |
| CS signal of serial pin | SPI_CS5 | 173 | 174 | LDM_Temp_SS2 | |
| Module flash data storage output | SPI_MISO5 | 175 | 176 | LDM_Temp_SS3 | |
| CS signal of serial pin | SPI_CS6 | 177 | 178 | LDM_Temp_SS4 | |
| Module flash data storage output | SPI_MISO6 | 179 | 180 | LDM_Temp_SS5 | |
| CS signal of serial pin | SPI_CS7 | 181 | 182 | LDM_Temp_SS6 | |
| Module flash data storage output | SPI_MISO7 | 183 | 184 | LDM_Temp_SS7 | |
| CS signal of serial pin | SPI_CS8 | 185 | 186 | LDM_Temp_SS8 | |
| Module flash data storage output | SPI_MISO8 | 187 | 188 | Input_KEY | Test button |
| Tri-color LED | STA_LEDR- | 189 | 190 | STA_LEDG- | Tri-color LED |
| STA_LEDB- | 191 | 192 | MCU_SDA | I2C SDA | |
| ADC detection | MCU_ADC1 | 193 | 194 | MCU_SCL | I2C SCL |
| MCU_ADC2 | 195 | 196 | GND | / | |
| 64 Groups of Serial Data Pin Definitions | |||||
| / | NC | 197 | 198 | NC | / |
| / | EXT_5V | 199 | 200 | EXT_5V | / |
| EXT_5V | 201 | 202 | EXT_5V | ||
| EXT_5V | 203 | 204 | EXT_5V | ||
Specifications
| Maximum Resolution | 1024×512@60Hz (For 8bit and 10bit video sources)620×512@60Hz (For 12bit video sources) | |
| Electrical Parameters | Input voltage | DC 3.8 V to 5.5 V |
| Rated current | 1 A | |
| Rated powerconsumption | 5 W | |
| OperatingEnvironment | Temperature | –20°C to +70°C |
| Humidity | 10% RH to 90% RH, non-condensing | |
| Storage Environment | Temperature | –25°C to +125°C |
| Humidity | 0% RH to 95% RH, non-condensing | |
| PhysicalSpecifications | Dimensions | 67.6 mm × 35.0 mm × 4.3 mm |
| Net weight | 10.4 gNote: It is the weight of a single receiving card only. | |
| Packing Information | Packingspecifications | An antistatic bag and anti-collision foam are provided for each receiving card. Eachpacking box contains 40 receiving cards. |
| Packing boxdimensions | 381.0 mm × 123.0 mm × 196.0 mm | |
Notes:
The amount of current and power consumption may vary depending on various factors such as product settings, usage, and environment.
When using the product, please ensure to use an aluminum heatsink plate with dimensions greater than 250.0 mm × 250.0 mm × 3.0 mm, or other methods that offer equivalent heat dissipation performance. Additionally, confirm that the material of the cabinet meets the necessary thermal requirements.